Notice:
Unfortunately the FunGene page is no longer available because the RDP server is dead and there are no plans to replace it. Before its demise RDP was looking for someone else to host FunGene and has an Amazon Machine Image nearly ready that might be used as the basis of a new website or as a “personal” stand-alone implementation. If interested, please contact me by email or using the contact form at the bottom of this page.
The Xander analysis pipeline is preconfigured for the genes rplB, amoA_AOA, AmoA_AOB, nifH, nirK, nirS, norB_cNor, norB_qNor, nosZ, nosZ_a2 and rplB. It is possible, however, to add other gene resource files to Xander by following the process given here.
First, go the the FunGene page (http://fungene.cme.msu.edu/) and see if your gene of interest has been already been entered. If not, you must select seed sequences covering the diversity of your gene. It requires some expertise to do this properly. Then contact the RDP staff (
http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/misc/contacts.jsp) and request that they add your seed sequences to FunGene. FunGene searches for related sequences and updates approximately monthly, so if your gene is not already listed it is important to submit seed sequences as soon as possible.
Reference sequence files and models for each gene targeted for assembly are placed in a gene reference directory. This directory is usually inside the Xander_assembler/gene_resource directory, but may be elsewhere if necessary (e.g. in your home directory on a cluster).
File organization
Under the gene_resource is a sub-directory is named for the gene; it contains several gene resource files and the subdirectory originaldata in this configuration:
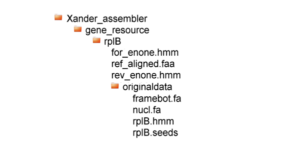
In this example, the gene directory is rplB. It contains three files and the sub-directory originaldata which in turn contains the four files required for preparing HMMs and for post-assembly processing. These four files are:
rplB.seeds: a small set of protein sequences in FASTA format, used to build forward and reverse HMMs for the gene. These seeds can be downloaded from FunGene.rplB.hmm: the HMM built from rplB.seeds using HMMER3.0 and can also be downloaded from FunGene.framebot.fa: a large near full length known protein set for identifying starting kmers and for FrameBot nearest matching.nucl.fa: a large near full length known set used by UCHIME for chimera checking.
For a new gene, all four of these files can be downloaded from the FunGene page at http://fungene.cme.msu.edu/index.spr.
Downloading Files from FunGene
- Go to the FunGene page and click on your gene of interest.
- Download the
gene.seedsandgene.hmmfiles using the links in the upper left of the FunGene gene page. - Click on “Display Options” in the upper right of the page.
- Change Sequences per page to 2000.
- Change Show Isolates/Environmental/Both to Isolate.
- Click on Update. This applies your changes and takes you back to the FunGene gene page.
- Click on Show/Hide filter options in the upper right of the page.
- Set Minimum HMM coverage to 80. More diversity is better. More sequences mean more starting points, requiring more computational time, but make the process of model creation less susceptible to noise. Click on Filter.
- Browse the results. You may find that definitions for some lower scoring sequences do not match your gene of interest. If so, you may further filter the display by entering a Minimum score under Show/Hide filter options and clicking on Filter again.
- Once satisfied with your filtering options, you can download the sequences. Beginning on page 1 (link in upper left), click on Select Entire Page in the upper left of the page. Assuming you are displaying 2,000 sequences per page, you may do this for up to 5 pages at a time. You may not download more than 10,000 sequences at a time.
- Next download the sequences by clicking on Begin analysis in the upper left of the page.
- Set Download with labels to accno.
- Set Download format to fasta.
- Uncheck the Aligned box.
- Select Protein download and click the Download button. Save the file.
- Select Nucleotide Download and click the Download button. Save the tile.
- If you had more than 10,000 sequences or 5 pages to download, return to your last page by selecting the appropriate page/tab in your browser. Click on Deselect All Sequences, click on the next page number, select all sequences, etc. and download the rest of the unalighned protein and nucleotide sequences.
- Put all of the files you downloaded in the originaldata directory for your new gene.
Dereplicate and Filter Sequences
Some further filtering of the downloaded sequences is required. FunGene collects duplicate sequences which should be removed by dereplication. Despite selecting isolates only, sometimes sequences for uncultured microorganisms are still present in the downloaded sequences and should be removed. Also, it is desirable to remove sequences with less than 50% identitiy to the closest seed sequence. The following code performs the necessary filtering after first catenating your downloaded files together if necessary. The python scripts are at https://github.com/jfq3/Auxillary-Xander-scripts. Edit the path to the python scripts and RDPTools as necessary.
#!/bin/bash
# If FunGene sequences are in parts, catenate the parts together.
echo "Catenating parts."
cat *_unaligned_protein_seqs.fa > protein.faa
cat *_unaligned_nucleotide_seqs.fa > nucleotide.fna
# Remove any uncultured sequences from FunGene protein sequences.
echo "Removing sequences from uncultured microorganisms."
python ~/scripts/filter_uncultured_seqs.py protein.faa uncult_protein.fa
# Remove duplicates:
echo "Removing duplicate protein sequences."
java -Xmx2g -jar /usr/local/RDPTools/ReadSeq.jar rm-dupseq -d -i protein.faa -o derep.fa
echo "Removing duplicate nucleotide sequences."
java -Xmx2g -jar /usr/local/RDPTools/ReadSeq.jar rm-dupseq -d -i nucleotide.fna -o nucl.fa
# Determine the proportional identity for each remaining sequence
# using the pairwise-knn sub-command to Alignment.jar:
echo "Determining identity to seed sequences."
java -Xmx2g -jar /usr/local/RDPTools/AlignmentTools.jar pairwise-knn -o knn_result.txt derep.fa *.seeds
# Filter out all sequences with proportional identity less than 0.5.
echo "Removing sequences if identity to closest seed is less than 0.5."
python ~/scripts/filter_knn_result.py knn_result.txt framebot.fa
You are now ready to prepare the gene reference files.
Prepare Gene Reference Files
The script prepare_gene_ref.sh, present in /RDPTools/Xander_assembler/bin/builds HMMs for Xander and aligns the reference sequences. The script does this using hmmer-3.0_xanderpatch, a modified version of HMMMER3.0 (see Installing RDPTools). The modified version is tuned to detect close orthologs.
- Inputs include three files from the
originaldatadirectory:gene.seedsgene.hmmframebot.fa
where
geneis the name of the gene. - Outputs are saved to the
genedirectory withingene_resourcefor_enone.hmm: forward HMM for assembling gene contigsrev_enone.hmm: reverse HMM for assembling gene contigsref_aligned.faa: contains the framebot.fa sequences aligned with for_enone.hmm and is used by Xander to identify starting kmers.
Copy prepare_gene_ref.sh from the Xander_assembler/bin directory to your scripts directory, for example to ~/scripts. Open the file in a text editor and edit the JAR_DIR, REF_DIR and hmmer_xanderpatch assignments to match your installation. The REF__DIR is the path to the gene_resource directory, not the sub-directory named for your gene. It does not have to be under Xande_assembler but should be for a local RDPTools installation.
Run the script. It takes a single argument, the gene name. Remember, if you change the location of the gene resource directory to build files for a different gene, you will have to edit this script again accordingly.
~/scripts/prepare_gene_ref.sh new_gene_name
It is important to manually examine the alignment of ref_aligned.faa using Jalview or another alignment viewing tool to spot any badly aligned sequences. If found, it is likely that there are no sequences in gene.seeds close these sequences. You need to determine if these problem sequences are actually from your gene of interest, and then either remove them or add some representative sequences to gene.seeds and repeat the preparation steps (including building gene.hmm with HMMER3.0). In some cases it will not be possible to get good alignments of ref_aligned.faa without dividing the seed sequences and framebot.fa into subsets. And of course, in such cases, the gene.hmm and other gene reference files need to be built for each subset of the seeds.
Test gene references
Check the file permissions for the files in the gene resource directory to be sure they are all readable by user, group, and world. If not, make them so (chmod 644 filename). Then test that your new gene resource files work by running Xander with a subset of nucl.fa as the sample sequences (SEQFILE). See section Test Local Xander Installation or Interactive Xander on MSU’s HPCC.
Add Taxonomy to framebot.fa
Once assured that your new gene resource files work, you can add taxonomy to the framebot.fa file. If taxonomy is added, Xander will automatically calculate the relative abundance of sequences classified by phylum.
- Requirements
- python 2.7
- Biopython 1.7.0
- Internet connection.
- (If necessary) Biopython can be installed with the following command:
sudo apt-get install python-biopythonor by following the instructions at https://pypi.python.org/pypi/biopython.
Workflow
- Create a directory and copy
framebot.fato it. For example, if you have been working on adding capability for the gene but, you might do the following:
mkdir ~/add_taxonomy
cd ~/add_taxonomy
cp /usr/local/RDPTools/Xander_assembler/gene_resource/but/originaldata/framebot.fa ~/add_taxonomy/
You may have to edit the path to framebot.fa depending on your FrameBot installation.
- Make a script
add_framebot_taxonomy.shwith the following code:
#!/bin/bash
# Configure the path to the pythonscripts directory:
scripts_dir=/usr/local/RDPTools/Xander_assembler/pythonscripts
# Parse the accession numbers to the file accnos.txt:
cat framebot.fa | grep ">" | sed 's/\(>\)\([A-Z0-9]*\)\(.*\)/\2/' > accnos.txt
# For each accession number in accnos.txt, download the GenBank file in xml format:
python $scripts_dir/fetch_ncbi_xml.py protein accnos.txt ./temp xml
# Parse the phylogenies from the xml files and write them to the
# framebot.fa sequence descriptions:
python $scripts_dir/parse_ncbi_lineage.py framebot.fa ./temp ./temp/framebot.fa
- Edit the script so that the path to the
pythonscriptsdirectory matches the path in your FrameBot installation. - Make sure the script is executable. If not, run
chmod 744 add_framebot_taxonomy.shto make it executable. - Change into the
add_taxonomydirectory. - Then, from the
add_taxonomydirectory, run./add_framebot_taxonomy.sh.
Outputs:
-
-
- Directory
tempunder your working directory (~/add_taxonomy/temp) framebot.fawith taxonomy in the temp directory
- Directory
-
- Replace the
framebot.fain thegene_resourcedirectory with this modified version; then Xander will be able to include taxonomy in its output.
